Contents
Thailand, a nation in Southeast Asia, is recognized for its colorful culture, breathtaking scenery, and kind people. The Thailand flag is a vibrant tapestry that weaves together a rich history and symbolic meaning. Not surprisingly, the flag is in the center of the country.
This article welcomes you on a riveting trip, digging into the enthralling narrative of the Thailand flag, and exploring everything from the meaning of its colors to the evolution of its design.
Thailand: Country Profile
Geography of Thailand
This intriguing nation tucked away in Southeast Asia proudly waves its colorful Thailand flag in the breeze. Thailand is a tourist destination that draws people from all over the world because of its breathtaking scenery, extensive cultural history, and friendly people.
Thailand’s wide coastline is bordered by clean beaches, sprawling plains in the center, and lush mountains in the country’s north. Nature lovers may discover the breathtaking grandeur of tropical forests, imposing waterfalls, and unique species in the nation’s national parks, including Khao Yai and Doi Inthanon.
Thailand is located in the center of Southeast Asia and has borders with Malaysia, Laos, Cambodia, Myanmar, and Laos. Due to its advantageous position, it has become a crossroads of cultures, fusing influences from adjacent nations to create a distinctive character.
Thailand observes the UTC+7 Indochina Time Zone (ICT). The nation does not observe Daylight Saving Time and sticks to a single time in Thailand throughout the whole year.
People & Culture
Thailand’s population, which is made up of several different ethnic groups, is thought to number roughly 69 million.
Although the majority are Thai, there are sizable communities of Chinese, Malay, and native hill tribes as well. The most populated urban area in Bangkok, the dynamic capital city, is renowned for its upbeat spirit, cutting-edge infrastructure, and historical sites.
The pleasant and outgoing Thai people are an important part of Thailand’s rich cultural heritage. The idea of “sanuk,” which stresses finding joy and pleasure in every part of life, is one that the country cherishes.
Thai food is renowned across the world for its exquisite taste balance and fragrant herbs. Thai cuisine is a joy for the senses, from the recognizable Pad Thai to the flavorful Tom Yum soup alongside a variety of delicious Thai snacks.
Theravada Buddhism, which is firmly ingrained in daily life in Thailand, has had a considerable influence on the country’s culture. There are several Buddhist temples located around the nation, many of which have elaborate construction and golden stupas. Saffron-robed monks may be seen performing religious ceremonies as the uplifting toll of temple bells fills the air.
The festivals of Thailand are an essential component of its cultural heritage. The Thai New Year, Songkran, is marked by joyful water battles intended to purge and cleanse the spirit. Thousands of floating lanterns are dropped into rivers during the Loy Krathong Festival of Lights as a way of letting go of negativity and making wishes for the future.
Thailand provides a variety of activities in addition to a rich cultural history. Every visitor can find something to do in Thailand, from learning Muay Thai, seeing ancient temples in Chiang Mai to enjoying island hopping excursions in Phuket.
Design & Symbolism Of Thailand Flag
The Thailand flag was meticulously designed to capture the spirit of Thailand via a harmonic fusion of hues, forms, and symbolism.
Colors
The Thailand flag is made up of five equal-width horizontal stripes that are placed from top to bottom. The flag’s use of strong, vivid colors conveys a sense of vibrancy and enthusiasm. Bright red top and bottom stripes are separated by white stripes that are each the same width. Between the two white stripes is a broader, brilliant blue stripe that serves as the center of the design.
Proportions
The Thailand flag’s proportionate aspect ratio is 2:3, meaning that the width is twice as large as the length. The flag’s height is split into five equal sections, each of which is occupied by a horizontal stripe. To maintain consistency and uniformity when displayed, the flag’s precise proportions are defined.
Color Symbolism
Each of the colors used in the Thailand flag has a deep symbolic significance. The nation of Thailand is represented by the red stripes, which stand for the people’s fortitude, strength, and resiliency. Red also represents the blood shed by the forefathers throughout their fight for freedom and independence. It is a potent reminder of the price they paid.
The Thai monarchy is represented by the center blue stripe, highlighting the significance of this institution in Thai culture. The color blue is connected to the monarchy and is used in the flag to honor the monarchy’s contribution to national unity and leadership.
Theravada Buddhism, which predominates in Thailand, is represented by the white lines that border the blue and red. The nation’s moral standards and spiritual traditions were influenced by Buddhism, and white is a hue that symbolizes purity, enlightenment, and righteousness. It is a reminder of how religious views live peacefully in Thai culture.
The placement of the stripes represents the harmony and unity of the Thai people. The monarchy’s crucial role in uniting the country is symbolized by the middle blue line, which is broader than the others. The red stripes on either side represent the inhabitants of Thailand, who are united by a shared sense of patriotism and national identity.
History of Thailand Flag
A remarkable representation of togetherness and national identity, the Thailand flag has a long and intriguing history. It has experienced major alterations over time, reflecting the political, cultural, and social developments in the nation.
Let’s travel back in time to examine the most significant turning points in the development of the Thailand flag.
Early Flags
Throughout its early history, Thailand, then known as Siam, had a number of flags. In the 17th century, during the rule of King Narai, the first identifiable flag appeared. This historic flag had a white chakra on a red background, which symbolized the Buddhist idea of the Wheel of Law.

The Chakra Flag
King Rama IV (King Mongkut) unveiled a new design in 1868, marking a crucial turning point in the history of the Thailand flag. The red field of this flag, often known as the Chakra flag, was kept, but the white chakra was swapped out for a blue one. The red chakra stood for the country, while the blue chakra represented the monarchy.
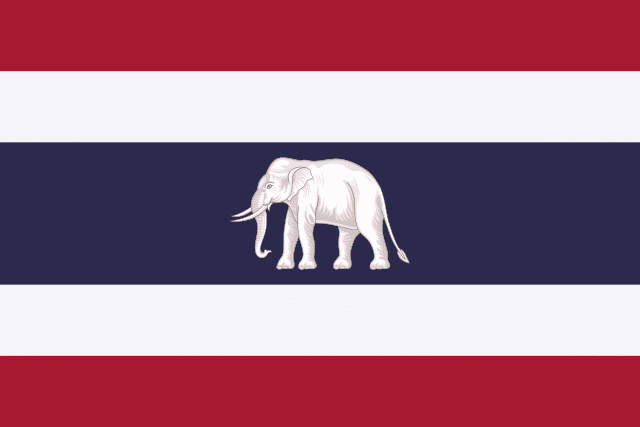
The Elephant Flag
In 1917, the flag underwent yet another change, this time under King Rama VI (King Vajiravudh). The respected national emblem of the white elephant stood out against a crimson backdrop in the Elephant flag. The flag was designed to promote patriotism and emphasize the nation’s rich cultural history.

The Triangle Flag
Thailand adopted a distinctive triangle flag during the brief years between 1917 and 1918. It had three horizontal bands: one at the top in blue, one in the middle in white, and one at the bottom in red. This unique style was intended to represent the nation’s transition to a constitutional monarchy.
The Trairanga Flag
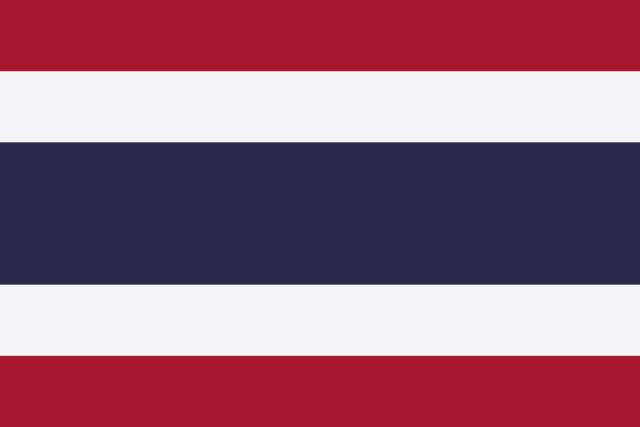
The formal adoption of the current design, known as the Trairanga, in 1919 was the most important turning point in the history of the Thailand flag. Five horizontal stripes make up the Trairanga: red, white, blue, white, and red. It was adopted as Thailand’s flag and represents the nation’s power, cohesion, and unity.
Current Thailand Flag
Except for slight changes to the color blue, the Trairanga has not been altered since it was adopted. The Thai flag, which symbolizes the Thai people’s dedication to their nation’s history and ideals, has stood the test of time as a symbol of pride and unification.

Interesting Facts About Thailand Flag
- Thailand’s flag is one of the few national flags in the world that is not rectangular, making it a flag with a distinctive shape. Instead, it adopts a recognizable 2:3 aspect ratio with five horizontal stripes.
- The Trairanga, the current Thailand flag, was formally adopted in 1919. One of Southeast Asia‘s first national flag designs hasn’t altered since then.
- The Thailand flag’s blue color has seen a few minor changes over time. It started off as a deeper tint, changed to a lighter one in the middle of the 20th century, and has been that way ever since.
- The Thai people have a high regard for their flag. It is carefully and precisely lifted and lowered. On different occasions, such as national holidays, regal ceremonies, and athletic events, the flag is conspicuously flown.
- The red, white, and blue hues of the Trairanga design were inspired by the French tricolor. This design decision was designed to represent the camaraderie that existed between France and Thailand in the early 20th century.
- The 28th of September is National Flag Day in Thailand. This day serves as a reminder of a united and proud nation and marks the adoption of the Trairanga flag.
Bottom Line
The Thailand flag is a lasting representation of togetherness and national pride in the “Land of Smiles.” Its vibrant colors, symmetrical pattern, and rich symbolism are a reflection of the Thai people’s fortitude, adaptability, and cultural history.
We are reminded of the power of solidarity and the tenacity of a country that proudly hoists its flag as we look at the red, white, and blue stripes. The Thailand flag serves as a symbol of optimism, pointing Thailand in the direction of a prosperous and peaceful future.